AWS Network Firewall Use Case
The fundamental purpose of a firewall is to establish a barrier between trusted internal networks and untrusted external networks. Firewalls are essential protections and threat prevention for all of our managed infrastructure. Some customers need inline threat prevention, control, advanced security capabilities like malware analysis and URL filtering, etc at the network layer, so that servers are protected from any malicious attack.
AWS Network Firewall Overview:
AWS has multiple networking services that enables to create a logically isolated network that we define, establish a private network connection to the AWS Cloud, use a highly available and scalable DNS service, and deliver content to our end users with low latency at high data transfer speeds with a content delivery web service. Security features within VPC include security groups (SGs), network access control lists (NACLs), routing tables and subnets, and gateways. Each of them is important to providing a secure, isolated network that can be extended through selective enabling of direct Internet access or private connectivity to another network.
AWS Network Firewall is a managed service to provide network protections for all of your Amazon Virtual Private Clouds to make sure that your traffic is inspected, monitored, and logged.
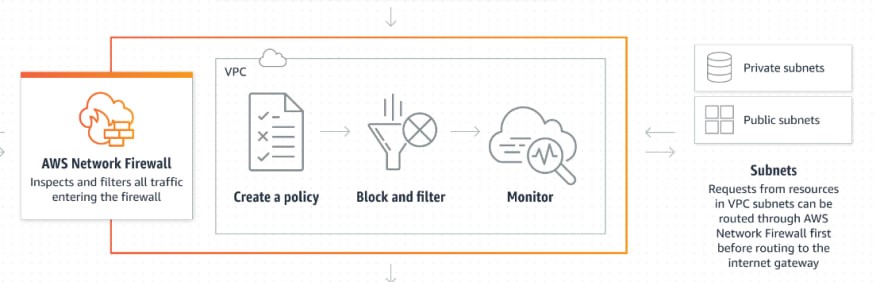
When AWS Network Firewall inspects a packet, it evaluates the packet against the rules in the policy’s stateless rule groups first, using the stateless rules engine. Then, depending on that inspection and on other settings in the policy, it might evaluate the packets against the rules in the policy’s stateful rule groups, using the stateful rules engine.
AWS Network Firewall – Sample configuration
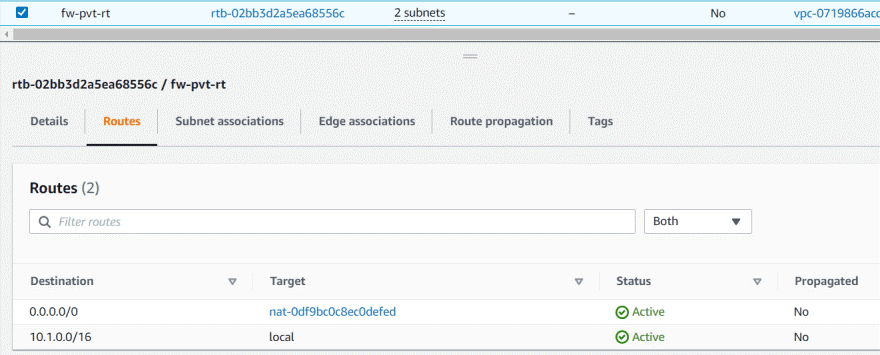
VPC route table for firewall
For Firewall we need a separate subnet, no other resource will be in this subnet
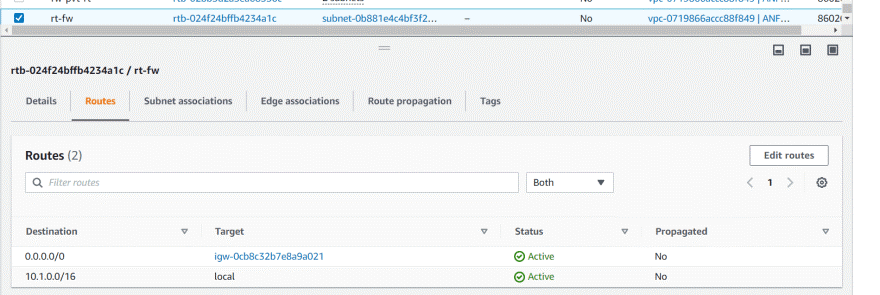
Public Subnet RT
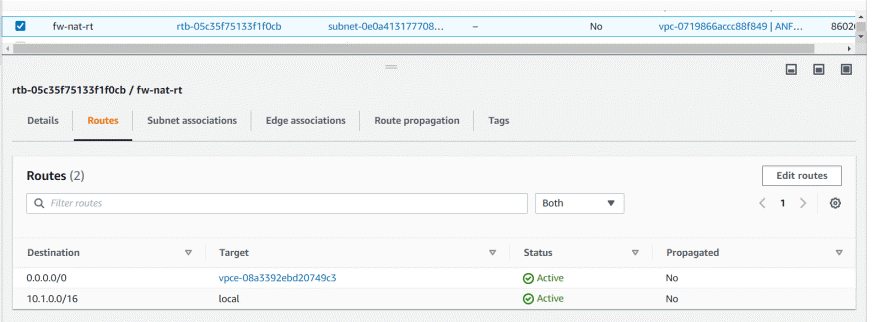
Private subnet rt
Private subnet traffic will go to NAT gateway
Firewall incoming RT
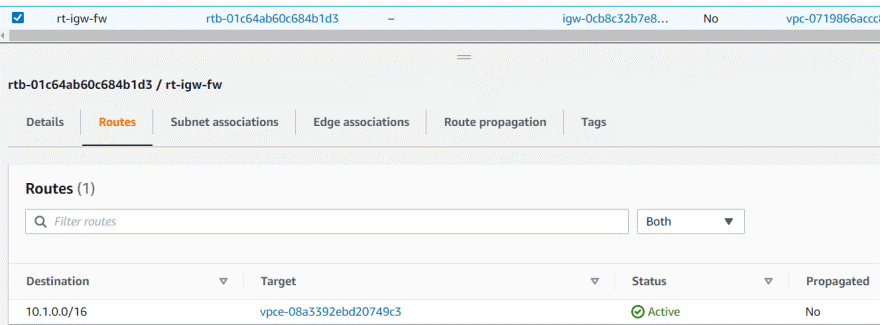
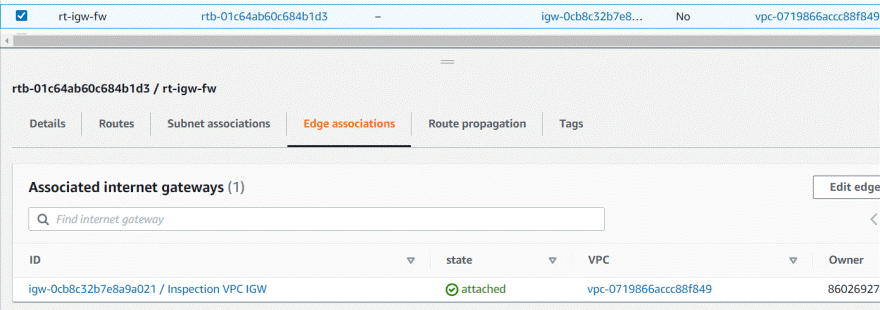
It requires edge association, no subnet association required.
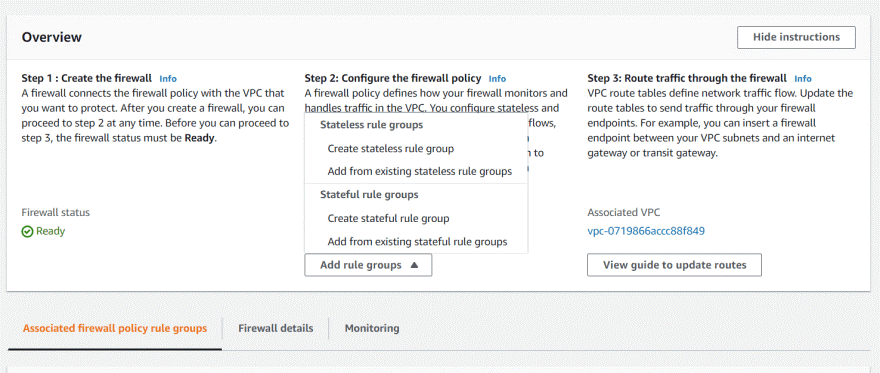
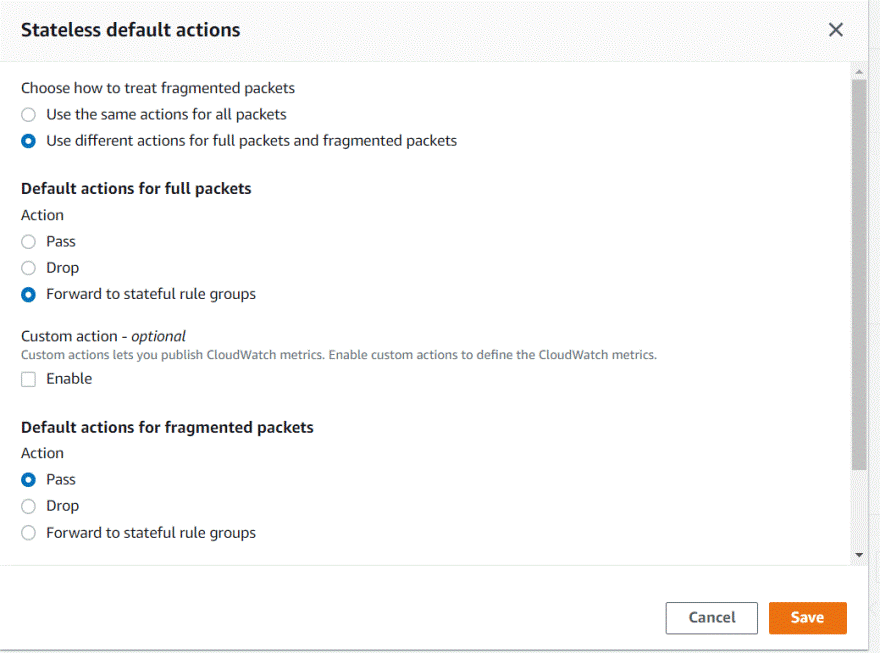
During stateless inspection, all individual packets in a flow are evaluated against all rule present in policy. Rules are processed in strict order based on the priority assigned to them, with lower numbered rules (e.g 10) taking precedence over higher numbered rules (for example, 100).
You are required to specify one of the following options:
Pass – Discontinue all inspections of the packet and permit it to go to its intended destination.
Drop – Discontinue all inspections of the packet and block it from going to its intended destination.
Forward to stateful rules – Discontinue stateless inspection of the packet and forward it to the stateful rule engine for inspection.
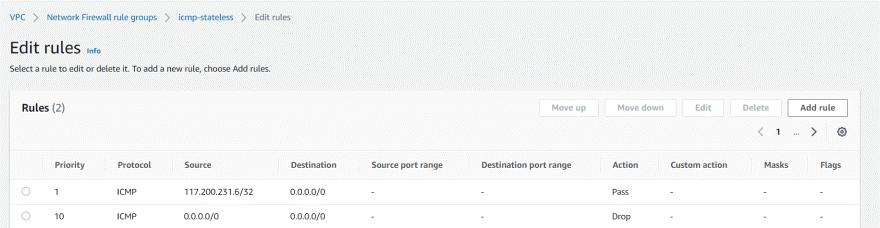
In the above rule group priority 1 rule having allow traffic from specific IP and deny all, however if we change the priority of 1 to 11 then , rule 10 will take precedence and all traffic will be dropped.
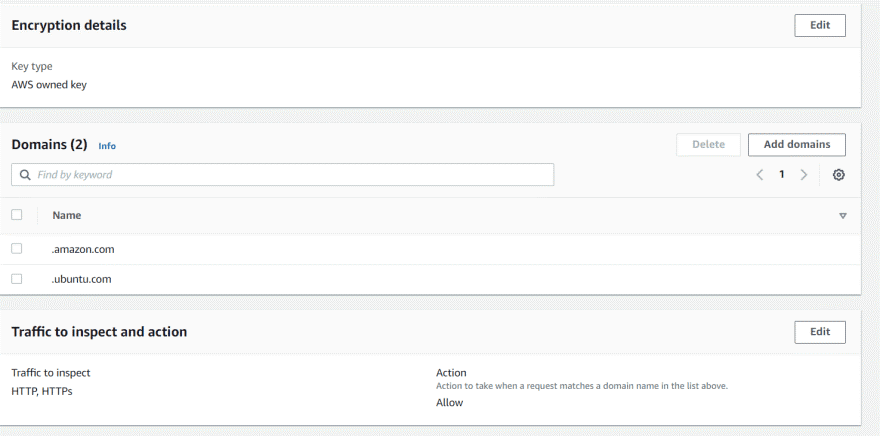
Stateful rule inspection works differently. The stateful rules engine processes rules in the order of action setting, with pass rules processed first, then drop, then alert. The engine stops processing if it finds the first match. E.g for approved domain list we can mention only certain domain can be accessed from the server restricting any other 3rd party repo access by developers.
The firewall also takes into consideration the order that the rules appear in the rule group, and the priority assigned to the rule, if any.
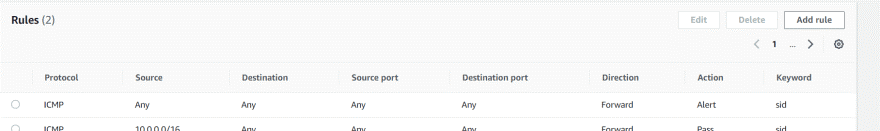
For example, a pass rule with a priority of 1 will be processed prior to a pass rule with a priority of 2. However, a drop rule with a priority of 1 will always be processed after all pass rules have been evaluated, including those with a lower priority.
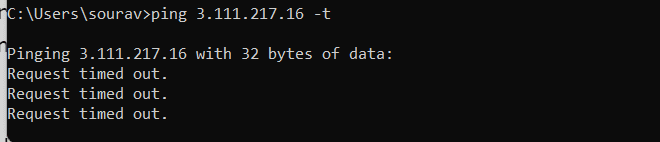
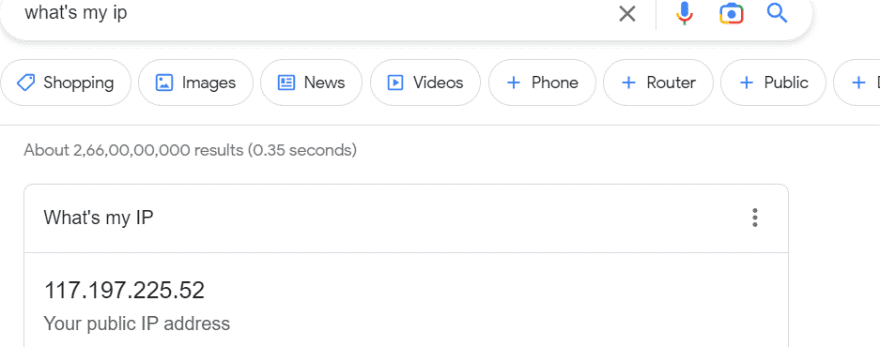
We can see in CloudWatch logs, traffic is blocked and captured in alert events.
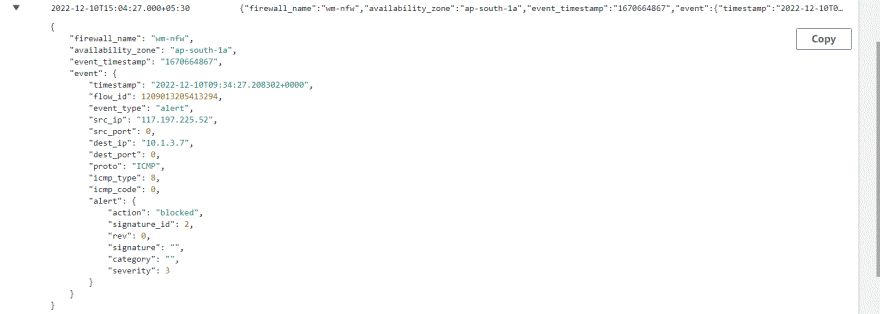
Conclusions:
AWS Network Firewall is an important product for large organizations who requires standard security practice and compliance. Combined with the other AWS security services like WAF, Guard duty etc. AWS Network Firewall which reduces attack surface by protecting VPC level , can be a good addition for SOC team. It’s easy to manage, block, or allow various traffic with firewall policies and set of rules.